Canada Medical Device Regulatory Pathway

Navigating the Medical Device Regulatory Pathway in Canada
Canada is one of the world's most trusted healthcare markets, and medical devices in Canada are regulated to the highest safety and quality standards. For companies planning to enter the Canadian market, understanding the medical device licensing process is critical.
This guide breaks down who regulates medical devices in Canada, the classification system, the licensing process, applicable fees, and review timelines.
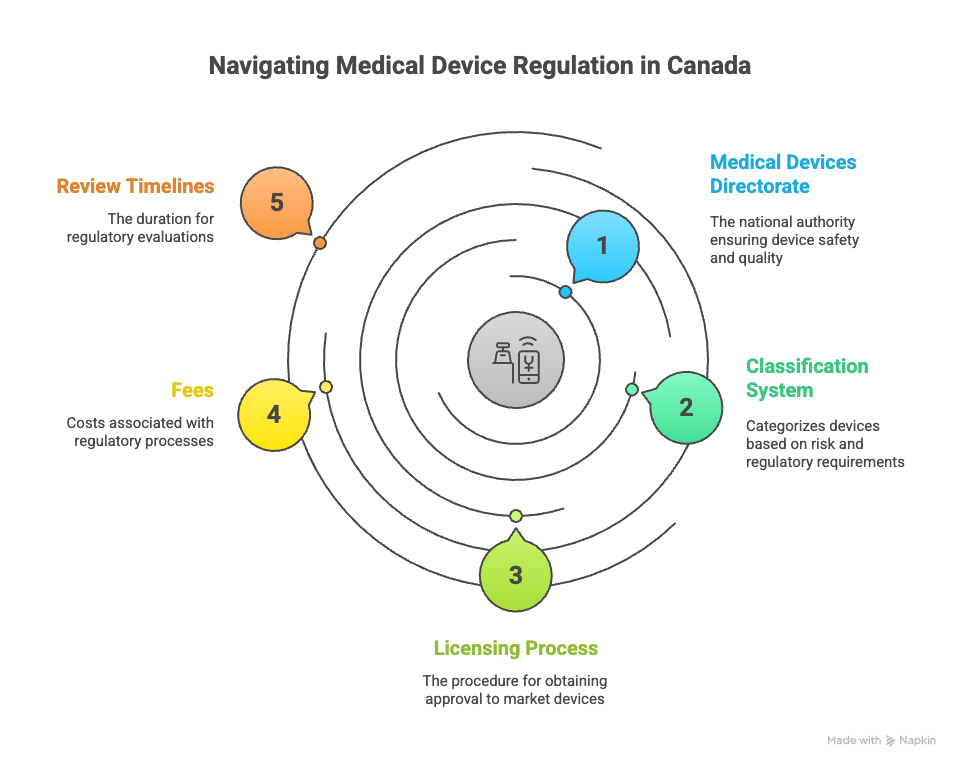
Who Regulates Medical Devices in Canada?
The Medical Devices Directorate (MDD), under Health Canada, is the national authority responsible for ensuring the safety, effectiveness, and quality of diagnostic and therapeutic medical devices.
MDD evaluates licence applications, monitors post-market safety, and enforces compliance with the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282) under the Food and Drugs Act.
What Do You Need to Place a Medical Device on the Market?
- Class I devices: Do not require a device licence. Instead, they are monitored through the establishment licensing process.
- Class II, III, and IV devices: Require a Medical Device Licence from Health Canada before they can be marketed.
Medical Device Classification in Canada
Medical devices are classified into four categories based on risk level:
- Class I: Lowest potential risk (e.g., stethoscopes, tongue depressors)
- Class II: Low-to-moderate risk (e.g., contact lenses, pregnancy tests)
- Class III: Moderate-to-high risk (e.g., ventilators, orthopedic implants)
- Class IV: Highest potential risk (e.g., pacemakers, HIV diagnostic tests) The higher the class, the more stringent the evidence and review requirements.
Prerequisites Before Applying for a Licence
Before submitting a medical device licence application, manufacturers must ensure the following:
- Complete the device licence application form and fee form (or authorize a regulatory correspondent).
- Sign and certify the accuracy of the application (faxed or e-signatures are acceptable).
- Submit the applicable licence fee (Class II, III, IV devices).
- Provide a valid Quality Management System (QMS) certificate.
- Include the licence application disclosure request.
Health Canada MDD regulatory pathway
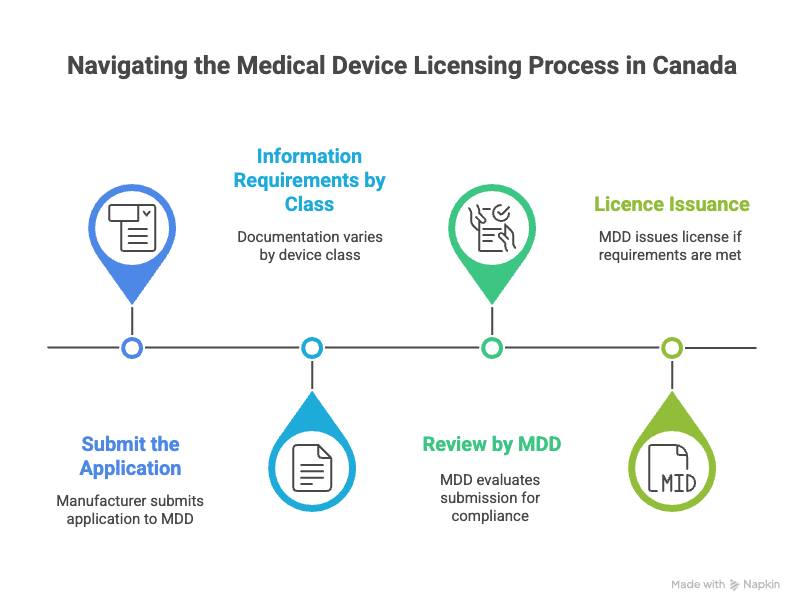
Step 1 - Submit the Application
The manufacturer submits the medical device licence application to MDD along with:
- Technical documentation (device description, safety and performance data)
- Quality Management System (QMS) certificate
- Licence application fee form
Step 2 - Information Requirements by Class
The amount of documentation and evidence required depends on the device class.
- Class II: Less detailed, focuses on QMS and compliance evidence
- Class III & IV: Require extensive clinical, safety, and performance data
Step 3 - Review by MDD
MDD evaluates the submission for compliance with the Medical Devices Regulations.
Step 4 - Licence Issuance
If requirements are met, MDD issues the medical device licence, authorizing market placement.
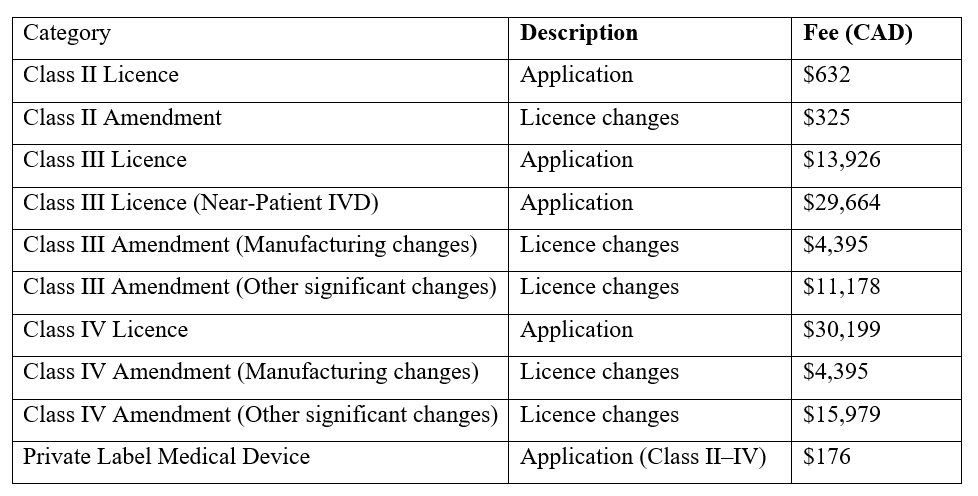
Fees for Medical Device Licence Applications (Effective April 1, 2025)
Review Timelines
Health Canada is committed to predictable review timelines:
- Class II: 15 calendar days
- Class III: 75 calendar days
- Class IV: 90 calendar days
Final Thoughts
Navigating the Canadian medical device regulatory framework can seem daunting, but it follows a structured and transparent pathway. Manufacturers should:
- Understand their device's classification
- Prepare complete and accurate documentation
- Plan ahead for timelines and costs By complying with Health Canada's requirements, manufacturers can ensure that their devices reach the Canadian market efficiently—while upholding the highest standards of patient safety.
Reference
- https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/medical devices/activities/fact-sheets/safe-medical-devices-fact-sheet.html
- https://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2021/sc-hc/H164-315-2021-eng.pdf
- https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/medical-devices/application-information/forms.html
- https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-98-282/
- https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/funding-fees/fees-respect-human-drugs-medical-devices/medical-device-licence-application-review-funding-fees-drugs-health-products.html
Share this blog
Read More Blogs

Understanding ICMED: India's Certification for Medical Devices


Saudi Arabia Medical Device Approval | SFDA Regulations


EU MDR and IVDR Medical Device Regulatory Pathway